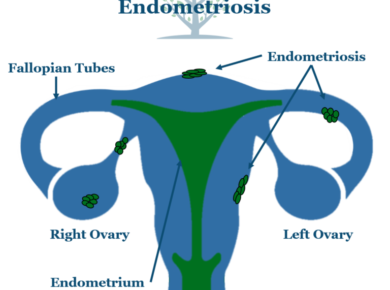
Talking about sex with your doctor isn’t always easy.
Nothing can kill the romance like talking about sexually transmitted infections (STI), yet we need to start.
It is important to know your body and what is normal for you. Paying attention to any changes is important to safeguard your sexual health and prevent the infection from spreading further.
So what is STI?
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are spread predominantly by unprotected sexual contact. STIs can also be transmitted during pregnancy, childbirth, and breastfeeding.
STIs have a profound impact on health. If untreated, they can lead to serious consequences including neurological and cardiovascular disease, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, stillbirths, and increased risk of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Most STIs are fairly common, and effective treatment is available — especially in the early stages.
Symptoms of STI
The majority of STIs have no symptoms. When present the common symptoms of STIs are :
Change in Genital Appearance
One of the reasons it is so important to know what is normal for your body is that knowing what is normal for you is the only way to determine if something has changed. Skin rashes, or clusters of red painful bumps on the skin, are quite common. Typically, they are caused by some irritation from the external environment, however, if the rashes appear near your genitalia, then it could be a cause for concern.
Pain during Sex or Urination
Pain during sex is usually the result of an STI or hormone imbalance. Common STIs like chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause inflammation which leads to pain during sex. Painful urination is associated with urinary tract infection. Bacteria can be spread into the female urinary tract during sex and lead to infection. Often frequent and painful urination can be signs of infection.
Change in Discharge
Discharge is extremely important for the health of the vagina. The vagina is self-cleaning. Glands in your vagina and cervix produce clear fluid that takes with it old cells and bacteria. Changes in vaginal discharge can point to infection-whether it is a sexually transmitted infection or another type such as a yeast infection. It is important to know what is normal for your body and look for changes in color, texture, and most importantly-smell.
Fevers
One symptom of HIV that most patients face is a high fever. Usually, about a week after the infection, the patient will experience a fever of about 39 to 40 degrees Celsius. Many patients may see this as a sign of dengue fever, but it could also be a sign of HIV. HIV and other STDs will make the body weaker as a result of the infection. It is important to seek medical help from STD clinics early as the medication will help prolong the lives of those with HIV.
Unprotected sex
Any time you choose to have sex without protection you are putting yourself at risk to contract an STI. Regular testing for STIs is a good idea for any sexually active adult, even if they are in a committed relationship.
If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, it is important to disclose to your healthcare professional that you have had unprotected sex, it can make for a speedier diagnosis and treatment.