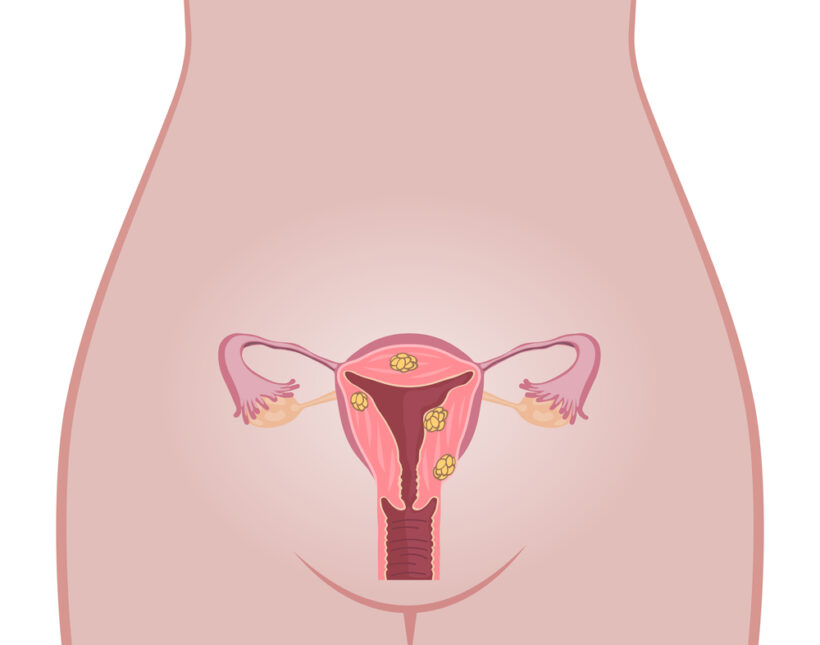
Uterine fibroids are benign (non-cancer) smooth muscle overgrowth in or around the womb (uterus). It is the most common tumor of the female pelvic organ with around 1 in 3 women developing them at some point in their life.
Uterine fibroids can occur at any time during a woman’s reproductive years. They most often occur in women aged 30 to 50.
What Causes Fibroids?
The exact cause is unknown, but they have been linked to the hormone called oestrogen. Furthermore, they also tend to shrink when the oestrogen levels are low e.g after the menopause
For some unknown reasons, uterine fibroid occurs 2 – 3 times more in black women particularly at an earlier age than in white women
Some of what may increase one’s risk of developing fibroids are:
- Obese women (due to the presence of increased estrogen)
- Early menstruation
- A first-degree affected relative (mother, sister)
- Hypertension
- Alcohol consumption
- Poor diet– A low intake of fruit and green vegetables
What do they look like and where are they located?
Fibroids can grow anywhere in the womb and also vary in size

What are the Symptoms of Fibroids?
Most people have no symptoms. They are routinely found during an examination or an ultrasound scan
Women who have symptoms (around 1 in 3) may have:
- Heavy periods or painful periods
- Abdominal pain
- Lower back pain
- Constipation
- Abdominal distension
- Painful sex
- Frequent Urination
- Infertility
- Miscarriage
- Foot swelling when the urine pipes (ureter) are compressed and this may lead to kidney failure
How are Fibroids diagnosed:
- Ultrasound scan (pelvic or transvaginal)
- A camera test to look into the womb through the vagina (hysteroscopy), sometimes through the belly (laparoscopy), and then a sample of the tissue may be taken to be examined (biopsy)
- Pregnancy and other routine blood tests
Management of Fibroids
Fibroids do not need to be treated if they are not causing symptoms.
Individuals with mild symptoms may be seen by general practitioners, while for others a specialist consult is advised
The treatment of uterine fibroids is usually individualized depending on the size and location of fibroids, age, symptoms, desire to have children, accessibility and affordability of treatment amongst others
Some of these treatments however have side effects that will be discussed by your treating physicians or surgeons
Pharmacological treatment
This involves the use of medication to treat symptoms such as:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding may be relieved by medication such as oral or injectable female hormones, an intrauterine device inserted through the vagina, medication to reduce bleeding, or painkillers
- Medication to shrink the fibroids- This may be prescribed for short-term use only usually before surgery. Consequently, the fibroids grow back once they are stopped
Surgical Techniques
This is usually advised when complications occur such as very low blood levels etc, fertility is affected, the fibroids are big or drugs alone are not sufficient. These are usually effective but there is also a chance of the fibroids growing back
The types of surgery include:
Myomectomy
This is the surgical removal of the fibroids. It can be done via open surgery or keyhole surgery using a thin telescope (hysteroscope) and small surgical instruments
Hysteroscopic morcellation of fibroids
The hysteroscope is inserted into the womb through the cervix and a specially designed instrument called a morcellator is used to cut away and remove the fibroid tissue.
Hysterectomy- Surgical removal of the womb
Non Surgical Techniques
- Uterine artery embolisation
This involves blocking the blood vessels that supply the fibroids by a radiologist, causing them to shrink.
- Endometrial ablation
This is the removal of the lining of the womb by using laser energy, a heated wire loop, or hot fluid in a balloon. It is not suitable for women who still desire children
- MRI-guided Percutaneous Laser ablation or Focused Ultrasound Techniques
These techniques use MRI to guide small needles into the center of the fibroid being targeted. Laser energy or ultrasound energy is passed through the needles to destroy the fibroid.
- Ultrasound-guided procedures
A long, thin device that has an ultrasound probe at the end is passed through the vagina, and heat is then applied to the fibroid to shrink it
To conclude, remember to share this with your loved ones and consult with a doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms.